Field Data Collection Made Easy with QField and ArcGIS Field Maps: A Step-by-Step Comparison
- Nithin B R

- Jun 17, 2025
- 3 min read
Updated: Dec 10, 2025
Introduction:
Field data collection is at the heart of effective GIS workflows — whether it's mapping property boundaries, documenting infrastructure, or conducting environmental surveys. Traditionally, this process involved manual forms, handwritten notes, and redundant data entry. Today, tools like ArcGIS Field Maps and QField allow you to collect structured data digitally, directly on-site, and link it to spatial features on a map.
This blog walks you through two practical, mobile-based solutions — highlighting how each streamlines residential or asset-based data collection.
Using ArcGIS Field Maps for Real-Time Data Capture
ArcGIS Field Maps integrates seamlessly with the ArcGIS Online environment, making it ideal for organizations already using Esri tools.
You begin by opening Field Maps Designer in your ArcGIS Online dashboard. This interface allows you to create a new map or configure an existing one.

Next, you select or create a hosted feature layer to store your field data and define attributes like Owner Name, Address, and Property Condition.

Once the feature layer is ready, the form-building interface lets you drag and drop various input types — text fields, dropdowns, yes/no switches, date pickers, and photo attachments. Required fields, read-only settings, and default values can also be configured for cleaner data input.


After publishing the map, you switch to the ArcGIS Field Maps mobile app, where the newly created map is available under "My Maps." You can tap on your location to add a new point.

The smart form pops up, allowing field staff to fill in the required details while capturing their current GPS location. Once submitted, the point along with its attributes is instantly synced to ArcGIS Online.

This approach eliminates manual data handling and provides immediate access to field data from your desktop or dashboard for analysis, review, and decision-making.
Using QField Cloud for Offline-First, Open-Source Surveys
QField is an open-source mobile GIS tool that connects directly with QGIS desktop projects. It’s ideal for situations where mobile teams operate in areas with poor internet access or when a free, customizable setup is needed.
The process starts in QGIS, where you create a new point layer and define fields relevant to your survey — such as House Number, Condition, and Image attachments.

To sync your project with the mobile device, install the QField Sync plugin from the QGIS Plugin Manager.

You then access the QField Cloud Projects Overview, where you can create an account or log in.

Click “Create New Project” and choose to convert your open QGIS project into a cloud project. Keep the default settings for the local directory and name your project.

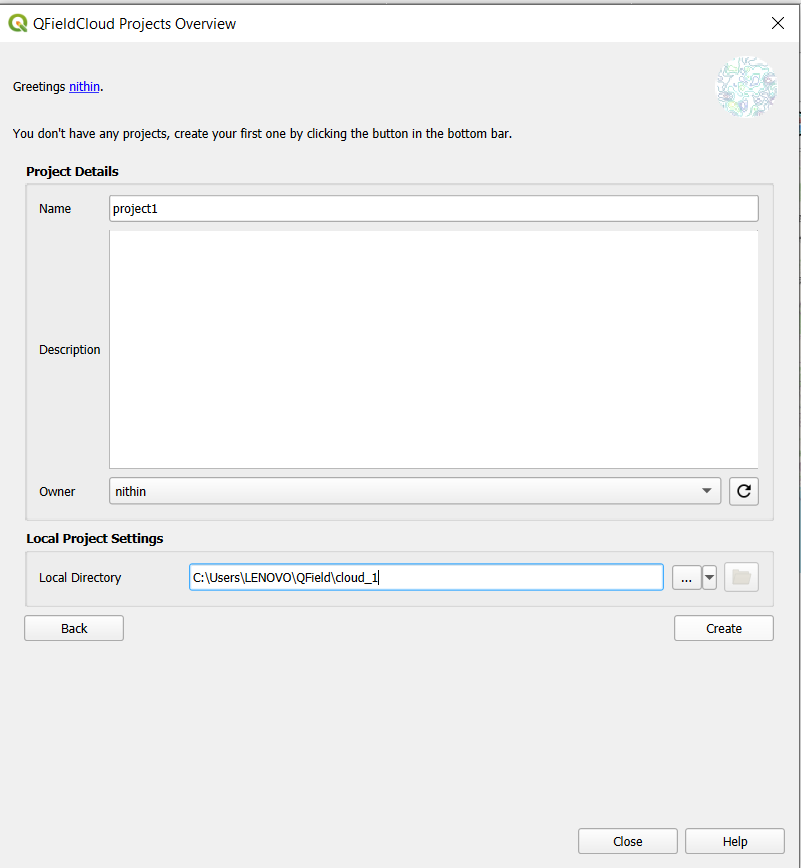
Once set, open the QField mobile app, log in, and download your project.

From the map interface, tap the menu in the top-left and enable digitization mode.

Using the green “+” button, you can now add a point feature on the map.

Immediately, the configured attribute form appears, and you can enter details, take a photo, and save the data.

To sync your data back, tap the cloud icon and push your updates to QFieldCloud.

On your desktop, go to QGIS and synchronize the cloud project. Use the “Prefer Cloud” option to retrieve your field data and finalize the sync.


This ensures all collected data — even if captured offline — is now part of your main QGIS project, ready for visualization and analysis.
Conclusion
With tools like ArcGIS Field Maps and QField, field data collection becomes faster, more accurate, and integrated. ArcGIS Field Maps suits teams needing real-time updates within an Esri ecosystem, while QField is ideal for QGIS users and remote conditions where offline work is essential.
By learning both, professionals can confidently handle diverse field conditions, different infrastructure types, and varying data requirements — all while eliminating paper forms and manual entry.
.png)


Comments