From CAD to GIS: A Practical Guide to Using AutoCAD Data in ArcGIS Pro
- Ajay K

- Jun 18, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Dec 10, 2025
Introduction
The convergence of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and GIS (Geographic Information Systems) has unlocked new possibilities for professionals working in urban planning, civil engineering, environmental management, and infrastructure development. AutoCAD is a widely used tool for designing and drafting, while ArcGIS Pro provides powerful spatial analysis and mapping capabilities. Integrating CAD data into GIS platforms like ArcGIS Pro allows for enhanced geospatial insights, decision-making, and project management.
Why Integrate CAD with GIS?
AutoCAD is excellent for design and detailed drafting, but it lacks the spatial intelligence that GIS brings. GIS enriches CAD data with geographic context, making it possible to:

Perform spatial analysis and overlay operations
Link attributes and metadata
Visualize projects in real-world locations
Enable multi-disciplinary collaboration across planning, utility, and environmental sectors
Preparing CAD Data for ArcGIS Pro
Before importing CAD files into ArcGIS Pro, some essential steps are recommended:
1. Clean and Organize the CAD File:

Remove unnecessary layers and objects
Ensure consistent layer naming and geometry
Use standardized coordinate systems (if available)
2. Convert to Supported Format:
ArcGIS Pro supports DWG, DXF, and DGN formats. Save the CAD file in a compatible format (preferably AutoCAD 2013 or later for best results).

3. Georeferencing the CAD Data:
If your CAD drawing lacks spatial reference, you can georeference it manually in ArcGIS Pro using control points or known coordinates.


Steps to Use AutoCAD Data in ArcGIS Pro
1. Add CAD Data to Map:
Open ArcGIS Pro
Insert a new map and use the "Add Data" tool to load the DWG or DXF file
The file will appear as a group layer containing point, polyline, polygon, annotation, and multipatch layers
2. Assign a Coordinate System:
If the CAD file lacks a defined coordinate system, assign one that matches your project’s spatial reference.
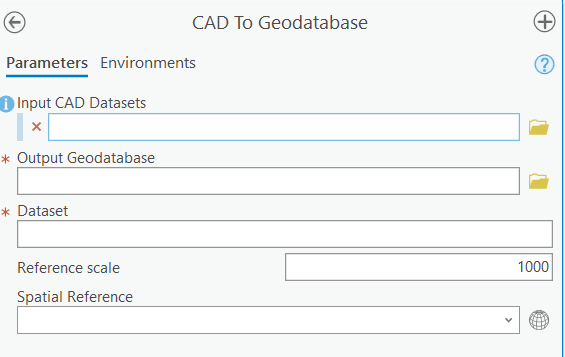
3. Convert CAD Features to Geodatabase:
Use the "Feature Class to Feature Class" tool to convert CAD features to geodatabase feature classes
This allows for easier editing, analysis, and integration with other GIS data
4. Symbolize and Analyze:

Apply symbology, add attributes, and perform spatial analysis
Integrate with other GIS layers such as satellite imagery, zoning maps, or environmental data
Real-World Applications
Urban Planning: Integrate AutoCAD building footprints with zoning data to evaluate compliance and land use.
Utility Mapping: Convert CAD drawings of electrical or water networks into GIS layers for easier maintenance and analysis.
Transportation Projects: Overlay road designs on topographic maps for impact assessments.
Oil and Gas Industry: In countries like the UAE, CAD-to-GIS integration is widely adopted for petroleum and gas infrastructure projects. CAD drawings of pipelines, rigs, and refineries are converted into spatial data layers to support asset management, environmental monitoring, and emergency planning. This approach ensures precise, data-driven planning in resource-sensitive environments.
Conclusion
Bridging the gap between CAD and GIS offers a unified workflow that combines precision design with spatial intelligence. ArcGIS Pro makes it seamless to import, convert, and utilize AutoCAD data, empowering professionals to move beyond static drawings and into the dynamic world of spatial decision-making. Whether you're planning a city, designing a highway, or managing utilities, integrating CAD into GIS ensures better outcomes and smarter solutions.
.png)



Comments